How Dapr helps to build a cloud-agnostic FaaS platform
What is OpenFunction
OpenFunction is an open-source, cloud-agnostic FaaS platform, accepted as a CNCF sandbox project on April 26, 2022. With OpenFunction, you can focus on your business logic without maintaining the underlying runtime environment. The OpenFunction community believes that functions should be able to run on any infrastructures or clouds.
Why a FaaS platform like OpenFunction needs Dapr
Dapr (Distributed Application Runtime) is a portable, event-driven runtime that makes it easy for any developer to build resilient, stateless, and stateful applications that run on the cloud and edge. Dapr helps developers tackle the challenges of building microservices and keeps the code platform-agnostic by embracing the diversity of languages and developer frameworks.
Nowadays, applications are mostly distributed applications. Dapr:
- Abstracts the common functionalities of distributed applications into various building blocks, such as bindings, pub/sub, and state management.
- Exposes these functionalities with unified HTTP or gRPC APIs.
Functions are also distributed applications with similar requirements, like input/output, pub/sub events, and get/set states. Unlike distributed applications, functions focus less concern on the underlying platforms or services, and more on business logic - exactly what Dapr tries to solve.
In the A Berkeley View on Serverless Computing paper, “Serverless” is defined as Serverless = FaaS + BaaS.
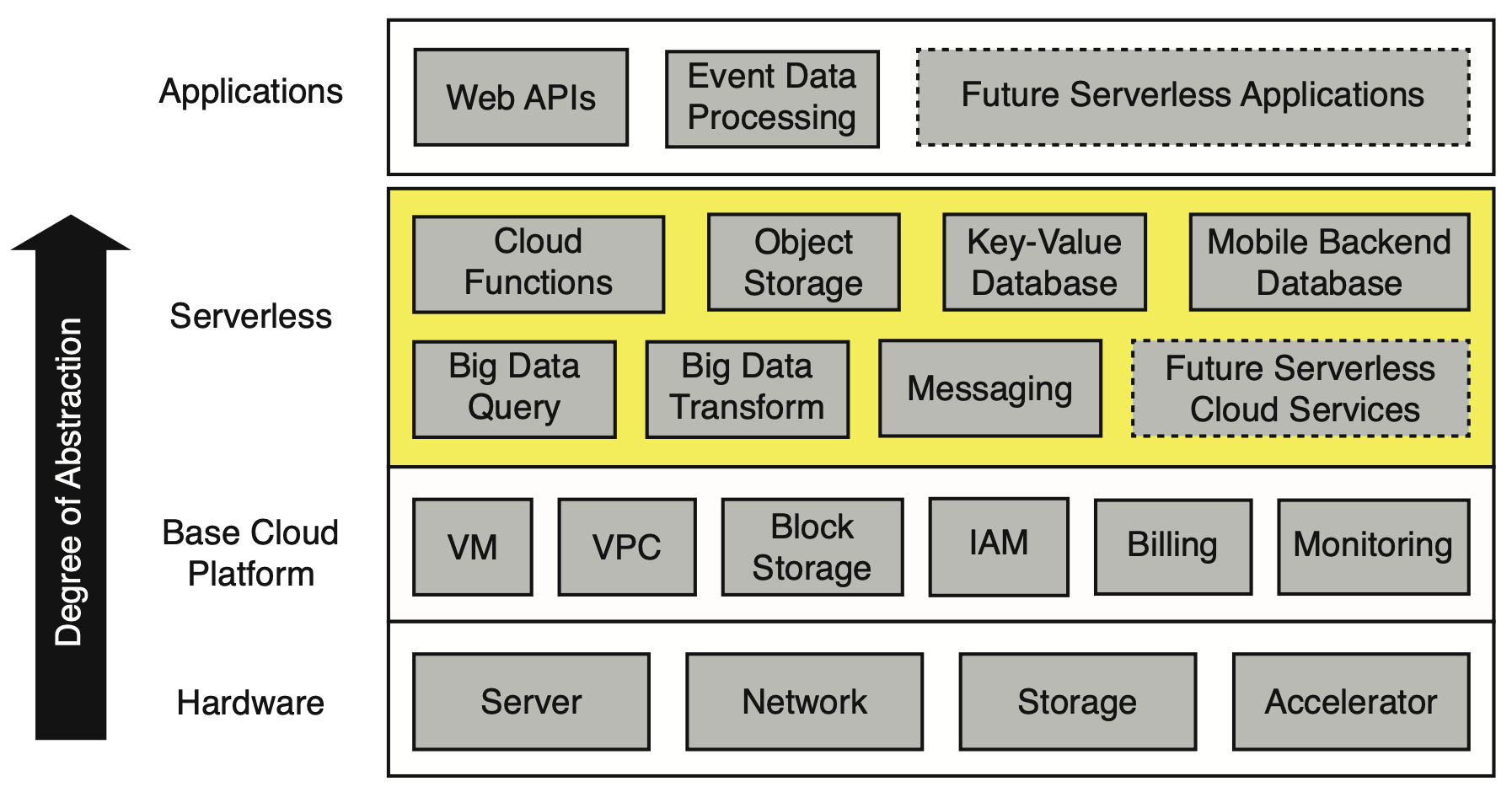
Usually a FaaS platform supports several languages and it needs to communicate with various backend services such as object storage, database, message queue etc. Let’s suppose a FaaS platform supports 5 languages and needs to communicate with 10 message queues.
- Without Dapr, each language will have to communicate with each message queue using this MQ’s own SDK which requires 5x10=50 implementations.
- With Dapr, each language only needs to communicate with Dapr using Dapr SDK and Dapr will handle the rest communication with different message queues which only requires 5x1=5 implementations.
As you can see from the above analysis, the complexity of a FaaS platfrom has been significantly reduced by introducing Dapr.
Dapr is actually another layer between FaaS and BaaS:
It acts as a unified interface for FaaS to various backend services:
Using Dapr in OpenFunction
OpenFunction is designed with several principles in mind that is open,flexible,and pluggable. This is where Dapr can help:
- By introducing Dapr, both sync and async function runtimes are able to utilize the power of distributed application runtime including input/output binding, pubsub, and state management etc. Different types of functions are able to communicate with various middleware, data sources like MySQL, PostgreSQL, Kafka, NATS Streaming, MQTT and cloud providers’ MQ in a unified, low cost and pluggable way.
- The EventBus of OpenFunction Events is built with Dapr’s pubsub building block, which enables users to use the message queue of their choice as the EventBus’s backend.
The Sync and Async function runtimes
OpenFunction supports two runtimes currently, the Knative Sync runtime and the OpenFunction Async runtime. Previously only OpenFunction Async runtime uses Dapr, and we added Dapr support to Knative Sync runtime as well in v0.6.0.
OpenFunction Async runtime
- Uses KEDA to trigger and autoscale async functions.
- Fetch input event from various Dapr input binding or pubsub components.
- Send functions output to Dapr output binding or pubsub components.
Here you can find a elastic log alerting async function sample:
- Kubernetes logs are collected and forwarded to Kafka
- An async function is deployed to find
404errors in log messages of wordpress pods in a specified namespace - An alert will be sent to Notification Manager whenever the async function find a
404error - Notification Manager will then send a notification to Slack
The async function is defined below, with familiar Dapr component definitions:
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta1
kind: Function
metadata:
name: logs-async-handler
spec:
version: "v2.0.0"
image: openfunctiondev/logs-async-handler:latest
imageCredentials:
name: push-secret
build:
builder: openfunction/builder-go:latest
env:
FUNC_NAME: "LogsHandler"
FUNC_CLEAR_SOURCE: "true"
# Use FUNC_GOPROXY to set the goproxy
# FUNC_GOPROXY: "https://goproxy.cn"
srcRepo:
url: "https://github.com/OpenFunction/samples.git"
sourceSubPath: "functions/async/logs-handler-function/"
revision: "main"
serving:
runtime: "async"
scaleOptions:
keda:
scaledObject:
pollingInterval: 15
minReplicaCount: 0
maxReplicaCount: 10
cooldownPeriod: 60
advanced:
horizontalPodAutoscalerConfig:
behavior:
scaleDown:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 45
policies:
- type: Percent
value: 50
periodSeconds: 15
scaleUp:
stabilizationWindowSeconds: 0
triggers:
- type: kafka
metadata:
topic: logs
bootstrapServers: kafka-server-kafka-brokers.default.svc.cluster.local:9092
consumerGroup: logs-handler
lagThreshold: "20"
template:
containers:
- name: function
imagePullPolicy: Always
inputs:
- name: kafka
component: kafka-receiver
outputs:
- name: notify
component: notification-manager
operation: "post"
bindings:
kafka-receiver:
type: bindings.kafka
version: v1
metadata:
- name: brokers
value: "kafka-server-kafka-brokers:9092"
- name: authRequired
value: "false"
- name: publishTopic
value: "logs"
- name: topics
value: "logs"
- name: consumerGroup
value: "logs-handler"
notification-manager:
type: bindings.http
version: v1
metadata:
- name: url
value: http://notification-manager-svc.kubesphere-monitoring-system.svc.cluster.local:19093/api/v2/alerts
Knative Sync runtime
- Sync functions is triggered by HTTP request, so Dapr is not used in sync function input.
- Whenever there are functions output requirements, sync functions can also send output to Dapr output binding or pubsub components.
Here is another function sample:
- Users send a HTTP request to a Knative Sync function.
- This sync function handles the request and then send its output to Kafka through a Dapr Kafka output binding or pubsub component.
- An async function is then triggered by this output event in Kafka (through a Dapr Kafka input binding or pubsub component)
This Knative Sync function is defined as below:
apiVersion: core.openfunction.io/v1beta1
kind: Function
metadata:
name: function-front
spec:
version: "v1.0.0"
image: "openfunctiondev/sample-knative-dapr:latest"
imageCredentials:
name: push-secret
port: 8080 # default to 8080
build:
builder: openfunction/builder-go:latest
env:
FUNC_NAME: "ForwardToKafka"
FUNC_CLEAR_SOURCE: "true"
srcRepo:
url: "https://github.com/OpenFunction/samples.git"
sourceSubPath: "functions/knative/with-output-binding"
revision: "main"
serving:
scaleOptions:
minReplicas: 0
maxReplicas: 5
runtime: knative
outputs:
- name: target
component: kafka-server
operation: "create"
bindings:
kafka-server:
type: bindings.kafka
version: v1
metadata:
- name: brokers
value: "kafka-server-kafka-brokers:9092"
- name: authRequired
value: "false"
- name: publishTopic
value: "sample-topic"
- name: topics
value: "sample-topic"
- name: consumerGroup
value: "function-front"
template:
containers:
- name: function
imagePullPolicy: Always
The Functions Framework
You don’t need to write any Dapr-specific code in sync or async functions to communicate with Dapr. You simply call the ctx.send method from the Functions Framework to send function output. Functions Framework will call the Dapr SDK to communicate with various Dapr input/output binding or pub/sub components.
Note: ctx.output for output binding and ctx.publish for pub/sub may be added in the future.
Currently, Dapr support has been added to Go functions framework and Nodejs functions framework. Dapr support to Python/Java/dotNet functions frameworks is still underway.
OpenFunction Events
Event-driven is one of the core features of a FaaS platform. Inspired by Argo Events, OpenFunction created its own OpenFunction Events. Unlike Argo Events, OpenFunction Events’ EventBus is decoupled with the underlying message queue implementation using Dapr pub/sub. This means you can use any message queue you prefer as EventBus, including Kafka, NATS Streaming, Pulsar, GCP pub/sub, Azure Event Hubs, etc.
Watch our sharing in Dapr community meeting for more details including a live demo for the sync & async functions.
Future
Although functions are usually considered to be stateless, state management is still important to a FaaS platform. OpenFunction will support the Dapr state management building block to enable functions to get/set states more conveniently. In addition, the recent workflow building block proposal might be used to implement the Serverless workflow spec.
Furthermore, if you would like to know how OpenFunction uses Dapr to build a FaaS platform for UISEE(an autonomous driving company) to handle their vehicle data, don’t miss our talk Empower Autonomous Driving with Cloud Native Serverless Technologies in KubeCon EU 2022.