A visual guide to Dapr
As a member of the Cloud Advocacy team within Developer Relations at Microsoft, I have the unique benefit of being able to hear about a lot of diverse technologies and solutions from folks who have hands-on expertise in their usage and development. So, when I heard my open source advocacy colleagues using the name Dapr alongside “cloud native” and “microservices”, I was intrigued.
And then I was delighted to discover Dapr stands for the “Distributed Application Runtime” and had just hit production-ready v1.0 status earlier this month. I wanted to know all about it. Thankfully, Dapr has extensive documentation to get us started. So I did what I always do when I want to learn something new – I distilled my learnings into one big picture, a sketchnote. And now, I want to share my initial learnings with you!
The big picture
I’ve said this before. Like 65% of users who are visual learners, I find that having key information captured in a single sheet can help me grasp the big picture before I dive into the details. Not only do I get a better sense of the various sides of that technology, but I get to “connect the dots” to other ideas or concepts that might be relevant in context. So, let me start by sharing the sketchnote (see below). You can download a higher-resolution version at the Cloud Skills: Sketchnotes website and check the Visual Azure blog for other visual guides to cloud computing technologies.
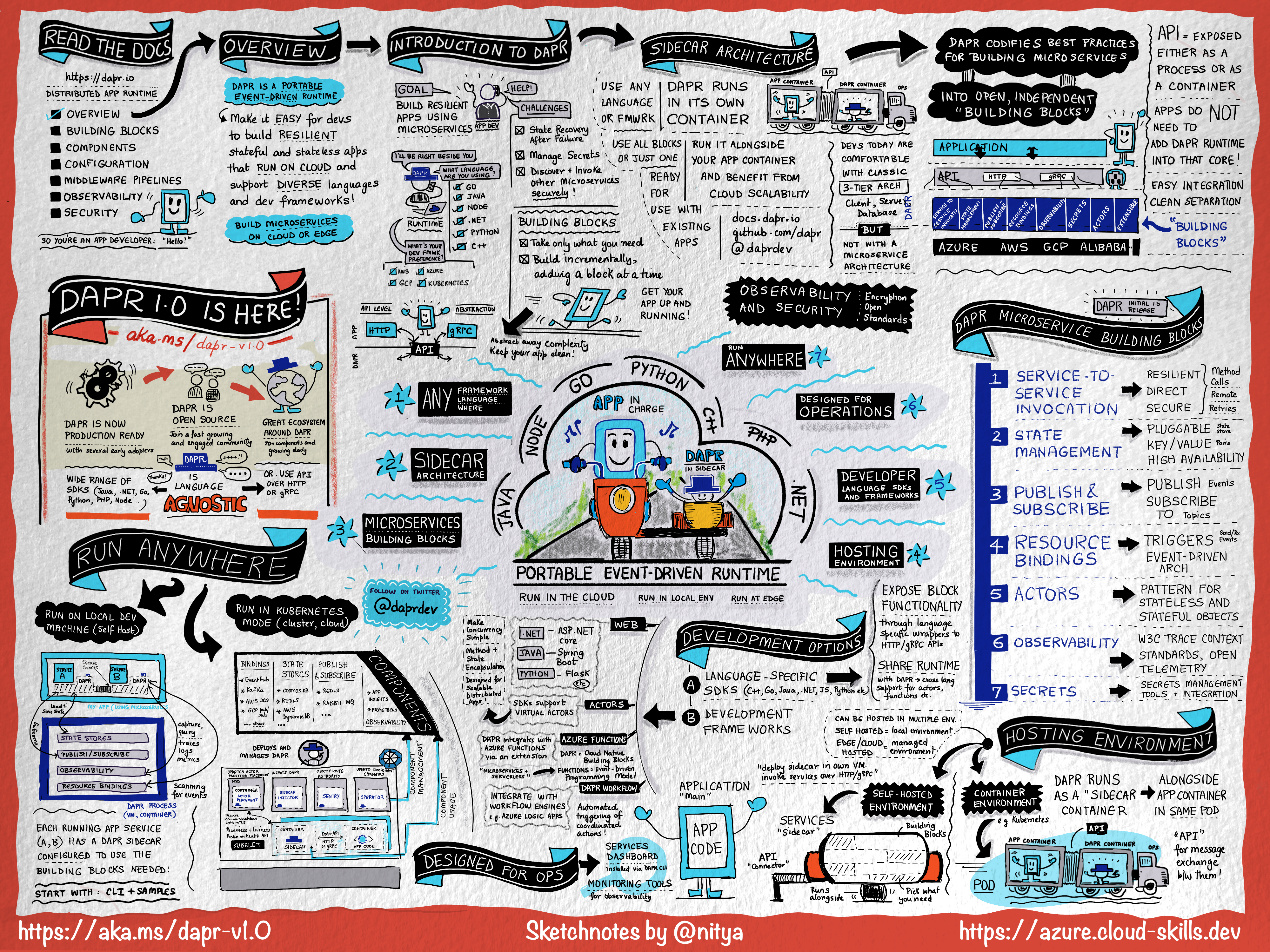
Key takeaways
The overview covers a lot of ground but here are the main points I took away:
What is Dapr?
Dapr stands for Distributed Application Runtime. It is a portable, event-driven runtime that makes it easy for app developers to build resilient stateless and stateful apps that can run on cloud and edge environments. More importantly, Dapr supports a diversity of programming languages and developer frameworks, offering us a quick starting point for experimentation and usage. You can get more details at the Dapr overview doc.
Why Use Dapr?
Many application developers have experience with traditional 3-tier (client-server-database) architecture. However, cloud native systems rely on loosely coupled systems and a microservices architecture designed to embrace large scale, rapid change, and resilient operation. Now, developers face a whole new set of challenges like discovering (and invoking) microservices, managing secrets, and recovering state after failures.
Dapr codifies best practices for building microservices into “building blocks” that are independent, open, and expose an API for easy integration and clean separation of concerns. Developers simply use a desired subset of these blocks, building incrementally to get their app up and running in record time.
How does Dapr work?
Dapr exposes its APIs as a sidecar architecture. In effect, Dapr can run in its own container or process alongside the main application. Your app doesn’t need to integrate Dapr into its core but can instead invoke building block APIs over HTTP or gRPC. This supplies a clean separation of app logic from microservices support services and makes it easier to scale your solutions - going from self-hosted (development) to cloud-hosted (VMs or Kubernetes) and edge deployments.
And while you can simply invoke those APIs using manually crafted HTTP or gRPC calls, you also have the benefit of having a rich set of language-specific SDKs that give you language-optimized typed APIs that are easier to integrate with, and test against. Currently supported language SDKs include C++, Go, Java, JavaScript, Python, PHP, Rust, and .NET! Note that Dapr itself is language-agnostic, supplying a default RESTful HTTP API that you can invoke directly if your preferred language SDK is not yet supported.
What else should I know?
Just three things:
- Dapr v1.0 is production ready! Dapr has several early adopters and the v1.0 release puts deeper focus on areas such as performance, security, high-availability and conformance. Read the release highlights here.
- Dapr is open source You can find the core runtime code, documentation, quickstarts and more on Github and community contributions are welcome! The Dapr Discord server and recurring community calls are a great way to engage with the community!
- The Dapr ecosystem is growing! There are 70+ components contributed by the community, so Dapr helps your application integrate with a wide range of technologies and also making it very portable for multi-cloud and hybrid scenarios.
The easiest way to get started, is to set up your local development environment (self-hosted mode) via this getting started tutorial and explore the provided quickstarts to learn the core concepts with code! And don’t forget to follow @daprdev on Twitter to get notified of updates and news!